60% of consumers putting the SDGs into action, including those who do not know about the SDGs
Dentsu Inc. (Tokyo: 4324; ISIN: JP3551520004; President & CEO: Toshihiro Yamamoto; Head Office: Tokyo; Capital: 74,609.81 million yen), has conducted its second Consumer Survey on the Sustainable Development Goals (hereinafter, "the survey"), which was carried out by Dentsu Team SDGs, a companywide working group tasked with promoting projects related to the SDGs1. The survey gathered data from 6,576 male and female respondents nationwide in Japan, aged between 10 and 79 years old.
The survey of course covered awareness and understanding of the SDGs, but also focused on specific behavior relating to the SDGs, and investigated the current status and changes occurring in relation to expectations vis-a-vis local government agencies and companies, the actual state of practical action toward the SDGs and obstacles to putting the SDGs into action, and the channels through which consumers come into contact with information on the SDGs.
The key findings of the survey are summarized by the following five points.
1. Overall awareness of the SDGs was 16.0%, an increase of 1.2 percentage points compared with 14.8% in the previous survey.2 Awareness among females was 11.6% (up 2.7 percentage points), and among males it was 20.5%. By occupation, students3 showed the largest increase in awareness, rising 11.4 percentage points.
2. Overall, 78.7% of respondents reported expectations that local government agencies would undertake initiatives relating to the SDGs, while more than half of respondents held similar expectations vis-a-vis companies. In particular, a high proportion of students (62.0%) expressed their intention to participate in or cooperate with activities carried out by local government agencies and non-profit organizations (NPOs).
3. Among all respondents, 60.4% reported that they were putting into practice at least some aspects of the thinking underpinning the 17 SDGs.
4. In terms of the structure of awareness and practice among consumers, the survey revealed the existence of four distinct segments: "conscious behavior" (6.5%); "preliminary knowledge" (9.5%); "unconscious behavior" (20.6%); and "low involvement" (63.4%). Consumers who did not have knowledge of the term "Sustainable Development Goals" but were still in some way putting the SDGs into action (unconscious behavior segment) accounted for 20.6% of overall respondents, which exceeded the percentage of consumers who were aware of the SDG terminology (16.0%).
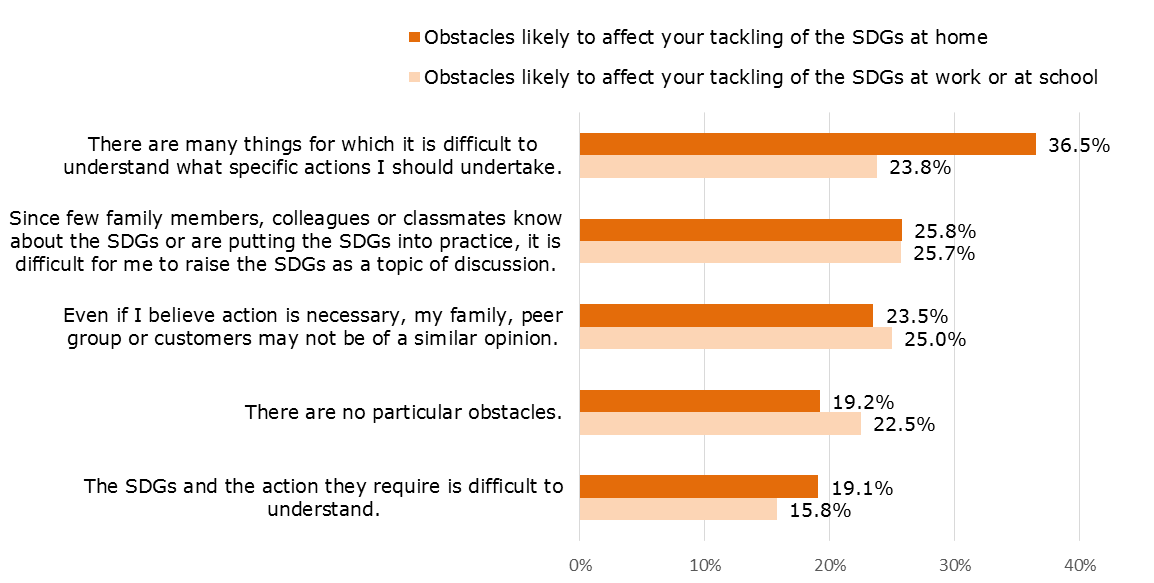
5. The obstacles reported by respondents to putting the SDGs into practice in the workplace, at school or at home were led by "difficult to understand what specific actions I should undertake," and "difficult to raise the SDGs as a topic of discussion." In the context of action at home, "difficult to understand what specific actions I should undertake" was cited by a conspicuously high proportion, at 36.5% of respondents.
Among the findings summarized above, one of the most striking features of the data gathered was elucidation of the existence of a segment of consumers with latent potential who are unaware of the SDGs but are nevertheless putting the goals into practice. By targeting communication programs at this segment, we believe that it will be possible to aim for increased awareness among consumers of the SDGs.
Notes:
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): The goals were adopted by the United Nations Sustainable Development Summit in September 2015. The 193 countries of the UN General Assembly set the SDGs with the aim of achieving the goals during the 15-year period 2016-2030. The SDGs comprise 17 goals and 169 specific targets agreed by all UN member countries with the objective of solving major global issues and building sustainable societies.
2. The first survey, conducted in February 2018, and the second survey summarized by this press release differ in sample size, survey area and other factors. Consequently, simple statistical comparisons cannot be made between the two surveys, and figures from the previous survey are provided for reference purposes only.
3. Students: This refers to the sum of elementary, junior high, senior high, college of technology, vocational, junior college, undergraduate university, postgraduate university, and other students.
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals
1. No Poverty
2. Zero Hunger
3. Good Health and Well-being
4. Quality Education
5. Gender Equality
6. Clean Water and Sanitation
7. Affordable and Clean Energy
8. Decent Work and Economic Growth
9. Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
10. Reduced Inequality
11. Sustainable Cities and Communities
12. Responsible Consumption and Production
13. Climate Action
14. Life Below Water
15. Life on Land
16. Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
17. Partnerships for the Goals
Details on the Five Key Survey Findings
1. Overall awareness of the SDGs was 16.0%, an increase of 1.2 percentage points compared with 14.8% in the previous survey. Awareness among females was 11.6% (up 2.7 percentage points), and among males it was 20.5%. By occupation, students showed the largest increase in awareness, rising 11.4 percentage points.
・ The high level of awareness among males was similar to the previous survey, but the breakdown by occupation shows an 11.4 percentage point rise in awareness among students (Reference data 1).
・ By occupation, executives and business proprietors had particularly high awareness (32.7%), and this was followed by public sector employees (25.3%), and students (24.8%) (Reference data 1).
・ By prefecture, awareness surpassed 20% in the following six prefectures: Okayama, Yamanashi, Ehime, Hyogo, Niigata and Osaka (Japan has 47 prefectures in total).
・ The channels through which consumers came into contact with information on the SDGs were ranked as follows: Web media (39.6%), newspapers (35.8%), television (25.2%), information gained through work or classes at school (18.0%), and magazines (15.5%) (Reference data 2).
・ According to the Japan Brand Survey 20194 conducted by Dentsu in December 2018, the average level of awareness of the SDGs among consumers surveyed in 20 countries and regions was 60.3%. Countries with the highest awareness were Italy (94%), India (81.3%), Indonesia and Vietnam (both 80.7%). Even in Russia, which had the lowest level of awareness, the rate was 36.3%. Continuing on from the previous year, awareness of the SDGs in Japan remains conspicuously low compared with the worldwide average.
Note 4. Japan Brand Survey: The objective of this survey is to track overseas consumer awareness and status regarding the "Japan brand" overall, including such aspects as cuisine, tourism and goods produced in Japan. Consumers in 20 countries and regions are surveyed, with respondents aged 20-59 years, and classified as middle or high income earners. Total sample size was 6,600 respondents, and research was conducted using an Internet-based survey (carried out in December 2018).
Reference data 1
Yearly comparison of awareness of SDG, by gender and occupation
(Question)
This question relates to the SDGs. Do you know the term "SDGs"?
Reference data 2
Channels through which respondents received information on the SDGs
(Question)
This question is for those who answered that they know the term "SDGs." Where did you read or hear about the SDGs? Please indicate the applicable categories shown on the right hand side (multiple categories possible).
2. Overall, 78.7% of respondents reported expectations that local government agencies would undertake initiatives relating to the SDGs, while more than half of respondents held similar expectations vis-a-vis companies. In particular, a high proportion of students (62.0%) expressed their intention to participate in or cooperate with activities carried out by local government agencies and non-profit organizations (NPOs).
・ The survey revealed a high level of expectations among consumers vis-a-vis the initiatives of local government agencies in relation to the SDGs. This included "I want the local government (area) where I live to be proactive in undertaking initiatives related to the SDGs" (78.7%), and "I want to support areas that have declared a commitment to the SDGs and are implementing related programs (77.4%) (Reference data 3).
・ With regard to central government and companies, more than half of respondents (58.3%) were of the opinion, "If initiatives are undertaken, the national economy and companies' businesses will grow." This expectation was held by a particularly high proportion of students (63.9%) (Reference data 4).
・ Furthermore, a relatively high percentage of students revealed a high level of motivation to put the SDGs into practice, responding, "I want to proactively participate in some way or cooperate with programs related to the SDGs implemented by local government agencies and NPOs" (62.0%) (Reference data 5).
Reference data 3
Expectations regarding local government agencies' initiatives for the SDGs
(Question)
Some local governments have already announced their own targets relating to the SDGs, and have begun to implement programs of some kind. Upon learning of these initiatives, please indicate your level of agreement with the statements shown below.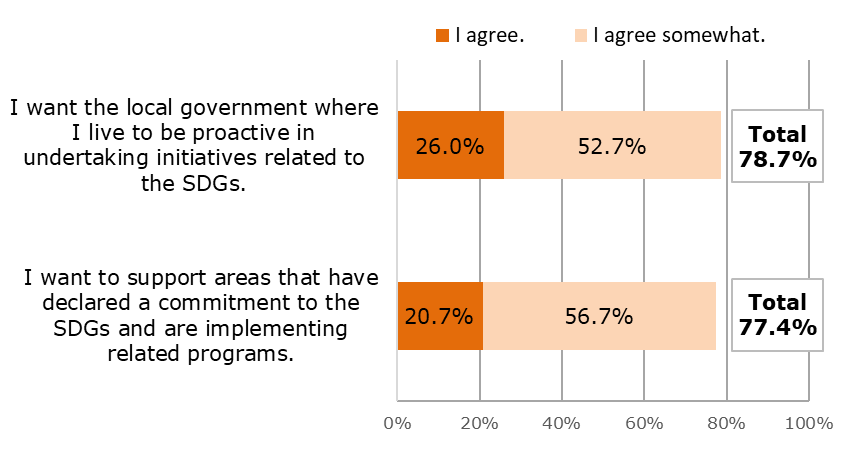
Reference data 4
Expectation regarding companies' initiatives related to the SDGs
(Question)
Please indicate your level of agreement with the statement shown below.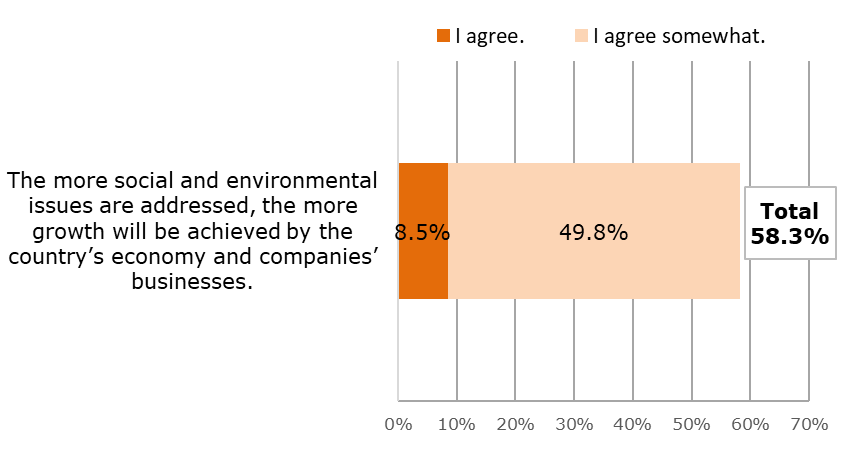
Reference data 5
Expectations vis-a-vis local government agencies' initiatives toward the SDGs, broken down by occupation
(Question)
Some local governments have already announced their own targets relating to the SDGs, and have begun to implement programs of some kind. Upon learning of these initiatives, please indicate your level of agreement with the statement shown below.
"I want to proactively participate in some way or cooperate with programs related to the SDGs implemented by local government agencies and NPOs."
3. Among all respondents, 60.4% reported that they were putting into practice at least some aspects of the thinking underpinning the 17 SDGs.
・ The following responses were defined as "putting into practice": "purchase of products of related companies or investment in such companies," "participation in or cooperation with related volunteer or NPO activities," and "putting into practice related actions on a personal level." An aggregate 60.4% of respondents reported that they had engaged in at least one of these practices (Reference data 6).
・ SDG number 3, "Good Health and Well-being" (35.5%) had a particularly high response rate (Reference data 7).
Reference data 6
Aggregate for putting SDGs into practice
(Question)
A total of 17 specific SDGs have been set with the objective of being achieved in all UN member countries. With regard to the SDGs, please indicate all of the items below that are close to your own thinking or behavior.
People who indicated that at least one of the following statements were applicable to them:
・ Purchase of products of companies that are related to these kinds of ideas, or investment in such companies
・ Participation in, or cooperation with, volunteer activities or NPO activities that are related to these kinds of ideas
・ Putting into practice on a personal level actions that are related to these kinds of ideas
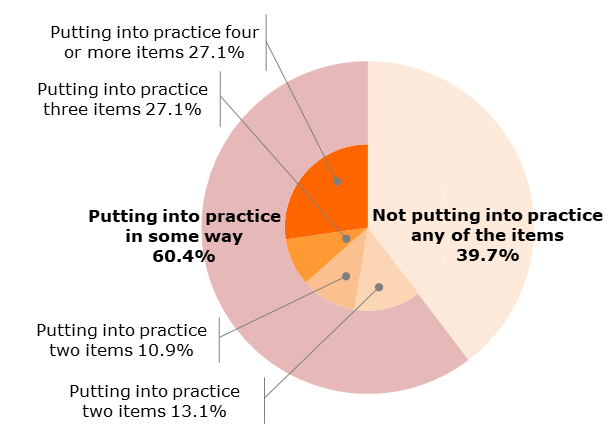
Reference data 7
Percentage of people putting each SDG into practice
(Question)
After reading the explanation of the SDGs, please indicate which SDGs shown in the list below are close to your thinking or behavior (multiple responses possible).
People who indicated that at least one of the following statements were applicable to them:
・ Purchase of products of companies that are related to these kinds of ideas, or investment in such companies
・ Participation in, or cooperation with, volunteer activities or NPO activities that are related to these kinds of ideas
・ Putting into practice on a personal level actions that are related to these kinds of ideas
4. In terms of the structure of awareness and practice among consumers, the survey revealed the existence of four distinct segments: "conscious behavior" (6.5%); "preliminary knowledge" (9.5%); "unconscious behavior" (20.6%); and "low involvement" (63.4%). Consumers who did not have knowledge of the term "Sustainable Development Goals" but were still in some way putting the SDGs into action (unconscious behavior segment) accounted for 20.6% of overall respondents, which exceeded the percentage of consumers who were aware of the SDG terminology (16.0%).
・ The "conscious behavior segment" accounted for 6.5% of respondents--people who were aware of the SDGs and reported putting into practice four or more of the SDGs. The "preliminary knowledge segment" accounted for 9.5% of respondents--people who reported putting into practice up to three of the SDGs.
・ The "unconscious behavior segment" accounted for 20.6% of respondents--people who were unaware of the term "SDGs" but were nevertheless putting at least four SDGs into practice (Reference data 8).
Reference data 8
Structure of awareness and practice
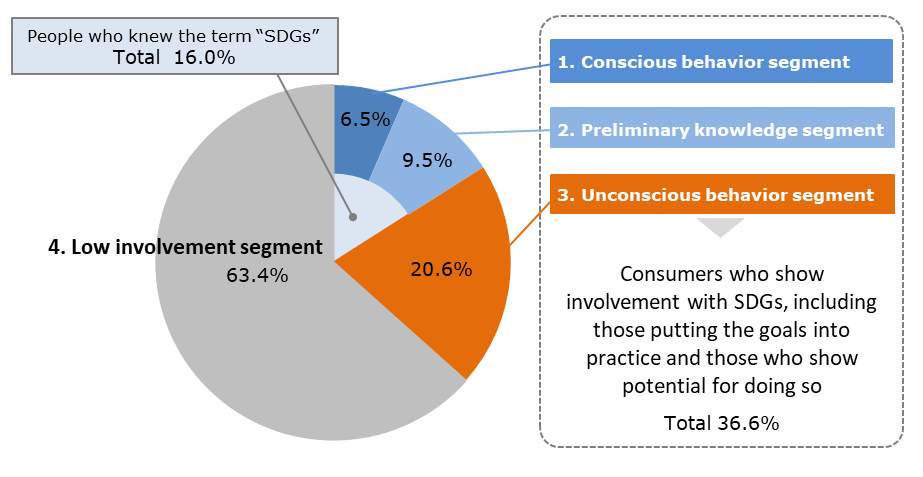
1. Conscious behavior segment refers to people who were aware of the term SDGs and were tackling at least four of the 17 SDGs.
2. Preliminary knowledge segment refers to people who were aware of the term SDGs but were tackling fewer than four of the 17 SDGs.
3. Unconscious behavior segment refers to people who were unaware of the term SDGs but were nevertheless tackling at least four of the 17 SDGs.
4. Low involvement segment refers to people who were unaware of the term SDGs and were tackling fewer than four of the 17 SDGs.
5. The obstacles reported by respondents to putting the SDGs into practice in the workplace, at school or at home were led by "difficult to understand what specific actions I should undertake," and "difficult to raise the SDGs as a topic of discussion." In the context of action at home, "difficult to understand what specific actions I should undertake" was cited by a conspicuously high proportion, at 36.5% of respondents.
・ With regard to obstacles at home, at work or at school, the following obstacles were cited most frequently: "It is difficult to understand what specific actions I should undertake;" and "Since there are few people who are aware of the SDGs or putting the SDGs into practice, it is difficult to raise the SDGs as a topic of discussion." The data suggest that the provision of information relating to the SDGs and action will likely lead to the arousal of action (Reference data 9).
Reference data 9
Obstacles to putting the SDGs into practice
(Question)
Please indicate all of the items that are close to your thinking as factors likely to become obstacles to tackling the SDGs at home. In addition, please indicate all of the items that are close to your thinking as factors likely to become obstacles to tackling the SDGs at work or at school (multiple responses possible).
That concludes our summary of the key findings of the survey. However, we received the following comment from the Director of the United Nations Information Center, Ms. Kaoru Nemoto. Part of her work involves promoting awareness of the SDGs in Japan.
Comment by Ms. Kaoru Nemoto
There was little change in overall awareness compared with the previous survey, but one of the encouraging aspects of the findings is the rise in awareness among young age segments, and among students in particular. Driven by an increase in educational opportunities for children in relation to the SDGs, I believe that we are not far off from the day when the SDGs become a common topic of conversation at home.
I also perceived in the findings the latent potential indicated by the fact that 20.6% of survey respondents were engaged in specific action relevant to the SDGs despite not having an awareness of the term Sustainable Development Goals. I believe that our tasks for the near future include helping these types of segments of consumers to understand the SDGs, and arousing everyday action from the current status in which businesses are taking the lead. In addition, I am concerned that the level of action in relation to Gender Equality (Goal 5) is low. The survey findings on this occasion indicate that the importance of Gender Equality requires a shift in consciousness and a transformation in people's thinking.
Outline of the Second Consumer Survey on the Sustainable Development Goals
Objective: Investigate the current status of awareness and understanding of the SDGs in Japan, as well as interest in the SDGs. Based on this, consider possible strategies for future promotion of awareness and action relating to the SDGs.
Survey area: Nationwide in Japan
Respondents: Males and females, aged between 10 and 79 years
Sample size: 6,576 persons
For analysis purposes, the sample was weighted in proportion to the distribution of population among Japan's 47 prefectures, and also in correspondence with the age group ratios present within Japan's population.
Survey method: Internet-based survey
Survey period: February 7-18, 2019
Survey institution: DENTSU MACROMILL INSIGHT, INC.
* The figures presented in graphs within this press release have been rounded to the nearest unit. Consequently, some totals do not match the sum of the data components shown.
###
